The Screwdriver Battery Does Not Charge From The Charger
The design of the charger from the screwdriver The design of the charger from the screwdriver Scheme, device, repair Without a doubt, the power tool greatly facilitates our work, and also reduces the time of routine operations. In progress
Scheme, device, repair
Without a doubt, the power tool greatly facilitates our work, and also reduces the time of routine operations. All kinds of self-powered screwdrivers are now in use.
Consider the device, the schematic diagram and the repair of the battery charger from the firm’s screwdriver “Interskol”.
First, let’s take a look at the schematic diagram. It is copied from a real charger PCB.
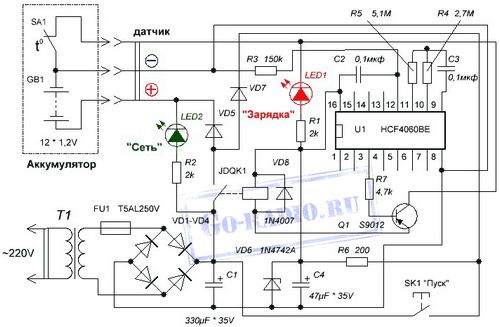
Charger PCB (CDQ-F06K1).
The power section of the charger consists of a GS-1415 power transformer. Its power is about 25-26 watts. I counted using a simplified formula, which I have already spoken about here.
The reduced alternating voltage 18V from the secondary winding of the transformer is fed to the diode bridge through the fuse FU1. The diode bridge consists of 4 diodes VD1-VD4 type 1N5408. Each of the 1N5408 diodes withstands a forward current of 3 amperes. The electrolytic capacitor C1 smooths out the voltage ripple downstream of the diode bridge.
The basis of the control circuit is a microcircuit HCF4060BE, which is a 14-bit counter with elements for the master oscillator. It drives a pnp bipolar transistor S9012. The transistor is loaded on the S3-12A electromagnetic relay. On the U1 microcircuit, a kind of timer is implemented, which turns on the relay for a given charge time. About 60 minutes.
When the charger is connected to the network and the battery is connected, the contacts of the JDQK1 relay are open.
The HCF4060BE microcircuit is powered by the VD6 Zener diode. 1n4742a (12V). The zener diode limits the voltage from the mains rectifier to 12 volts, since its output is about 24 volts.
If you look at the diagram, it is not difficult to notice that before pressing the button “Start” U1 HCF4060BE microcircuit de-energized. Disconnected from the power supply. When the button is pressed “Start” the supply voltage from the rectifier is fed to the 1N4742A zener diode through the resistor R6.
Further, the reduced and stabilized voltage is supplied to pin 16 of the U1 microcircuit. The microcircuit starts to work, and the transistor also opens S9012, which she controls.
The supply voltage through the open transistor S9012 is supplied to the winding of the JDQK1 electromagnetic relay. The relay contacts close and supply voltage is applied to the battery. The battery starts charging. Diode VD8 (1N4007) bypasses the relay and protects the S9012 transistor from a reverse voltage surge that occurs when the relay coil is de-energized.
The VD5 diode (1N5408) protects the battery from discharge if the mains supply is suddenly turned off.
What happens after when the button contacts “Start” open? The diagram shows that when the contacts of the electromagnetic relay are closed, the positive voltage through the diode VD7 (1N4007) is fed to the Zener diode VD6 through a damping resistor R6. As a result, the U1 microcircuit remains connected to the power source even after the button contacts are open.
The design of the charger from the screwdriver
Replaceable battery.
The GB1 replaceable battery is a unit in which 12 nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd) cells, each 1.2 volts, are connected in series.
In the schematic diagram, the elements of the replaceable battery are circled with a dotted line.
The total voltage of such a composite battery is 14.4 volts.
A temperature sensor is also built into the battery pack. In the diagram, it is designated as SA1. In principle, it is similar to the thermal switches of the KSD series. Thermoswitch marking JJD-45 2A. Structurally, it is fixed on one of the Ni-Cd cells and fits tightly to it.
One of the terminals of the temperature sensor is connected to the negative terminal of the storage battery. The second pin is connected to a separate, third connector.
What can be done when the car battery is not charging
The first step is to find out the cause, and only then take action to eliminate it. To do this, you need to measure the voltage at the battery terminals, check the level, density of the electrolyte and its color. Also, of course, a visual inspection of the surface of the battery, auto-wiring is necessary, and it is mandatory to determine the current leakage.
Let’s consider in detail the possible consequences of each of the reasons for poor battery performance, and also determine the actions that need to be done in a given situation:
Contact terminal oxidation both prevents good contact and promotes leakage current. As a result, we get a fast discharge or an unstable / absent charge from the generator. There is only one way out. To check not only the condition of the battery terminals, but also on the generator and the vehicle weight. Strongly oxidized terminals can be removed by cleaning and lubricating oxides.
Malfunction in the generator (belt, regulator, diodes).
Broken belt You would probably have noticed, but the fact is that even a slight slack in the tension can contribute to slippage on the pulley (as well as oil ingress). Therefore, when powerful consumers are turned on, a light on the panel may light up and the battery will be discharged, and on a cold engine, a squeak is often heard from under the hood. This problem can be eliminated either by stretch or by replacement.
Diodes in a normal state, they should pass current only in one direction, checking with a multimeter will make it possible to identify a faulty one, although they often simply change the entire diode bridge. Incorrectly functioning diodes can cause both undercharging and overcharging of the battery.
When the diodes are normal, but they get very hot during operation, it means that the battery is being overcharged. Responsible for stress regulator. It is better to change it right away. In a situation where the battery is not fully charged, you need to pay attention to the generator brushes (after all, they wear out over time).
Deep discharge, as well as with a slight shedding of the active mass, when the battery does not want to be charged not only on the car from the generator, but even the charger does not see it, you can make a polarity reversal or give a high voltage so that it grabs the charge.
This procedure is often performed with AVG batteries when its terminals are less than 10 volts. The polarity reversal allows a completely discharged battery to start. But this will only help if the poles on the battery have really changed, otherwise you can only do harm.
Changing the battery poles (both lead-acid and calcium) occurs in the event of a complete discharge, when the voltage of some battery cells with a lower capacity than others, connected in series, decreases much faster than others. And having reached zero, as the discharge continues, the current for the lagging elements becomes charging, but it charges them in the opposite direction, and then the positive pole becomes a minus, and the negative pole becomes positive. Therefore, by changing, for a short time, the terminals of the charger, such a battery can be brought back to life.
But remember that if the pole change on the battery did not occur, then if there is no protection on the charger against such a situation, the battery can be permanently damaged.
This process will not work if:
- The plates fell off and the electrolyte became cloudy;
- One of the cans is closed;
- There is no required density of electrolyte in the battery.
Desulfation is well done by the polarity reversal method, but only no more than 80-90% of the capacity can be restored. The success of this procedure lies in thick plates, thin ones are completely destroyed.
The density of the electrolyte is measured in g / cm³. Checked with a densimeter (hydrometer) at a temperature of 25 ° C, should be 1.27 g / cm³. It is proportional to the concentration of the solution and inversely dependent on the ambient temperature.
Note that the density of the electrolyte in the battery must be the same in all sectors. And if in any of the cells it is strongly lowered, then this indicates the presence of defects in it (in particular, a short circuit between the plates) or a deep discharge. But when such a situation is observed in all cells, then it is a deep discharge, sulfation, or simply obsolescence. A very high density is also not good. It means the battery was boiling from overcharging due to the failure of the generator. Which also adversely affects the battery. To eliminate problems caused by uneven density, you need to service the battery.
Features of car battery maintenance
A set of instructions for the correct maintenance of various types of car batteries. Features of servicing helium, alkaline and acid batteries
details
With sulfation there is a deterioration or lack of contact of the electrolyte with the plates. Since the plaque blocks access to the working body, then battery capacity drops dramatically, and recharging it does not give any result. The voltage either increases very slowly or does not change at all. Such the process is irreversible.
But sulfation at the initial stage can be overcome by a series of cycles of full charge with low current and full discharge with minimum current (for example, by connecting a 12V 5W bulb).
Closing one of the cans is a consequence of the collapsed plates and the appearance of sludge at the bottom of the battery. When trying to charge such a battery, there will be a strong bubbling of the electrolyte, as with a full charge. The defective section will boil but not recharge. There is nothing to help here.
How do you know if the battery is not charging?
The battery does not charge from the generator. The first signal that the battery is not being charged is a lit red battery light! And in order to make sure of this, you can check the battery voltage. The battery terminals should be 12.5. 12.7 V. When the engine is started, the voltage will rise to 13.5. 14.5 V. With the consumers on and the engine running, the voltmeter readings, as a rule, jump from 13.8 to 14.3v. The absence of changes on the voltmeter display or when the indicator goes beyond 14.6v indicates a generator malfunction.
When the generator is running but not charging the battery, the reason may be hidden in the battery itself. Apparently it was completely discharged, which is called “zero”, then the voltage is less than 11V. Zero charge can occur due to sulphated plates. If sulfation is insignificant, you can try to eliminate it. And try to charge with a starting-charger.
How to understand what the battery does not charge from the charger? When the battery is connected to the charger, evidence that it is fully charged is the constantly changing voltage at the terminals and the jumping voltage or current indicators on the dial of the device. If the charge does not go, then there will be no change. When there is no charging to the storage battery from the Orion-type charger (which has only indicators), then very often you can observe a hum and a rare blinking of the “current” light.
The car battery is not being charged by the generator. Why?
Common reasons when the battery does not charge from the generator are:
- Oxidation of the battery terminals;
- Stretched or broken alternator belt;
- Oxidation of wires on the generator or vehicle ground;
- Failure of diodes, voltage regulator or brushes;
- Sulfation of plates.
The most obvious reasons why your battery won’t charge
There is little awareness that the battery is not charging; it is also necessary to understand the causes of such a problem. It should be noted that in some cases the battery is fully charged, but after charging it sits down very quickly. In this case, the reason may be hidden in an electrical leak, which could happen due to the unplugged dimensions or interior lighting.
If the reason is still in the battery, then, most likely, sulfitation of its plates led to this. They were covered with a white coating, which is lead sulfate in a coarse crystalline form. If the sulfitation is minor, it can be easily eliminated.
If the battery, in principle, is not charged from the charger and generator, then the reasons may be oxidation of the terminals, breakage of the alternator belt, or oxidation of the wires that are on the alternator belt.
Terminals oxidized
In fact, this is one of the most common and commonplace reasons that the battery is not being charged either from the charger or from the generator. If a whitish coating appears on the terminals, it will greatly increase their resistance, so charging will not occur.
You can remove this plaque, only you need to act very carefully. To do this, take the finest grit sandpaper and gently walk over the affected terminal surface. It should be understood that lead, from which the terminals for car batteries are made, has a very soft structure, therefore, under the influence of friction, it can easily break. In addition, if the terminals leak from cleaning, it will then be difficult to clamp them.
Broken alternator belt
Another reason that the battery does not charge from the generator may be a break in its belt. By the way, sometimes even its weakening and slipping on the pulley can lead to the same result. The battery will only be discharged. If the belt is really broken, you can see it with the naked eye. You can fix the problem by replacing it.
If the belt just began to slip during operation, not giving the battery the required amount of charge, then the reasons can be very different. This may be due to the fact that it is heavily worn out, and due to the fact that its natural stretching has occurred during operation.
If the belt is worn out, it must be replaced. In all other cases, you can tighten the belt a little and observe the operation of the generator and battery. If charging proceeds normally, let the belt continue to function in the position to which you pulled it.
Oxidation of wires on the generator
If the battery does not charge, then the reason may also be the oxidation of the generator wires. In this case, the situation can be saved by ordinary stripping, which is carried out using the same sandpaper.
But the wires can not only oxidize, but also break off or burn out as a result of a voltage drop. The smell of burnt insulation will help you determine if the wires are burned out. In this case, you will have to become an electrician for a while and replace the burnt wires, having previously determined the cause of the incident and eliminated it. If you replace the wires and do not solve the problem, the situation can repeat itself with even more serious consequences.
Reasons for poor battery charging and how to fix them
- Reasons for poor battery charging and how to fix them
- Battery is not charging: how to find out?
- The most obvious reasons why your battery won’t charge
- The battery does not charge from the charger: we check the external factors of the malfunction
- We are looking for malfunctions in the battery and fix them
- Maybe the reason lies in the generator?
Many drivers have had to deal with the problem when the car battery starts to fail. Discharged, stood on the charge, worked for several hours and again showed zero charge. Or, in general, when connected to a charger, the battery charge does not increase. In such a situation, you should not rush to throw the battery in the trash, since the problem may still have a solution. And the first thing to do if the battery is not charging is to find the cause of the problem, which we will do.
- Battery is not charging: how to find out?
- The most obvious reasons why your battery won’t charge
- The battery does not charge from the charger: we check the external factors of the malfunction
- We are looking for malfunctions in the battery and fix them
- Maybe the reason lies in the generator?
We are looking for malfunctions in the battery and fix them
When the generator is running but not charging the battery, the reason may be hidden in the battery itself. Car battery malfunctions can be very different, so we will consider them in more detail.
Sulfated
If the battery does not charge and at the same time shows a zero charge, it is possible that the reason lies in the sulfation of its plates. We have already mentioned this above, here we will give another way that will help to cope with this problem and return the batteries to life:
1. Flush the battery with distilled water and remove any debris from it.
2. Let the battery dry completely and charge it if possible.
3. Bring the density of the electrolyte to 1.285 g / cm3, for which it is worth using a liquid with a density of 1.4 g / cm3.
4. Do not allow the electrolyte to boil or overheat!
Five. Continue charging the battery until the charge in each section reaches 1.3-1.4 V.
6. We make the charging current two times lower, but continue charging.
7. If the voltage on the sections and the density of the electrolyte remain unchanged for two hours, the charging process can be stopped.
8. Add electrolyte and distilled water.
Nine. With the light bulb on, we reduce the voltage on each section to 1.7 V.
After this procedure, the battery should begin to work fully. Nevertheless, in addition to sulphation, the reason that the battery does not charge may lie in the destruction of its plates. In this case, the electrolyte should turn black during charging. Often, the plates are also closed, which can be learned from the lack of electrolyte in one of the sections, which for this reason usually begins to heat up strongly.
Why the screwdriver battery does not charge. Causes and elimination
The reasons for the absence or weak level of charge, as well as ways to eliminate the malfunction, are different:
- There is no contact between the terminals of the charger and the battery. This is a consequence of the fact that the memory plates are bent. Gently bend the plates back to working condition.
- Oxidation of terminals or dirt adhering to them. Contacts are cleaned and wiped with alcohol.
- Failure of one of the “cans”. Disassemble the battery pack housing by removing the cover (unscrew the screws or remove the latches). Call each jar with a tester for voltage or discharge current. With tension it is easier. It is either there or not, but this method does not always work. The discharge current is measured on a load resistor. In a faulty can it is an order of magnitude lower than in a working one. After diagnostics, the faulty can is separated from the serviceable ones, and a new one is installed in its place, exactly of the same type, and with the same polarity orientation relative to the other elements.
There is one more reason for the lack of charge, but it is typical only for nickel-cadmium batteries. The memory effect has worked, and the battery does not charge, although its resource has not yet been exhausted. In order not to bring it to this, it is important to carry out the charging correctly.
What to do if the screwdriver battery does not charge
Cordless screwdrivers are more convenient to use than mains. They are distinguished by their mobility, independence from the presence of an outlet “at hand”, the length of the cord. The only drawback is that you need to monitor the charge level for timely recharging. But not all types of batteries allow you to do this, and at the most inopportune moment the screwdriver stops working. And, unfortunately, there comes a time when the battery stops charging.
Battery types
There are three types of tool batteries:
- Nickel Cadmium (NI-Cd). The older generation, which is still equipped with household screwdrivers. Affordable price, good ratio of size and capacity (rather compact), keep the charge in an idle state for a long time. The disadvantage is the memory effect. If you recharge without a full discharge, then “information” about an incomplete volume is accumulated, it interferes with giving a charge until the real resource is exhausted.
- Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-Mh). An improved analogue of nickel-cadmium batteries with a cleaner production technology. Although the memory effect is present, it is weaker. The main disadvantage is that they are quickly discharged during storage.
- Lithium ion. The most advanced type, which is gradually replacing other types in the segment of professional / semi-professional electric hand tools. High capacity, almost complete absence of “memory”, durability, low self-discharge in storage mode. The only drawback is the high cost compared to other analogs.